Lesson 1:
Introduction to Print Design for Fashion
-
- Learning how to prepare allover prints
- Learning how to prepare placed prints
- Get a taste and ability in using graphic elements and color
- Understand the link between creativity and feasibility
- Mastering the technical knowledge of printing for own creative needs
NB: for each class is mandatory to bring laptop and any physical material needed, listed or asked by the lecturer the class before.
-
1) Introduction: Overview of course structure and objectives. List of materials and documents required for the final exam project.
2) About print design: Printing techniques
3) Review: Brief discussion on students’ collection themes and initial ideas.
4) Homework Assignment
-
1. Develop a first research and create a print design moodboard for your project.
2. Upload the file in JPG format to Google Drive before the next session.Field Research Assignment:
1. Visit vintage shops or museums to gather inspiration.
2. Collect physical or digital images of textiles, fabrics, or prints that could inspire their final projects.3. Bring to next class.
Course Introduction
-
This course is designed to equip students with specialized skills in print design for fashion. The goal is to foster creativity, personal interpretation, and innovation, while ensuring coherence with each student’s thesis project. Students will develop prints from initial drafts and graphic concepts through to final files, ready for production.
-
• Fundamental techniques of textile printing.
• Development of allover and engineered prints.
• Design of soft accessories and CMT placement for ready-to-wear.
• Graphic identity and chromatic cohesion with the thesis collection.
• Practical projects aimed at combining creativity with professional print design skills.
-
The course will mainly involve the use of Adobe Photoshop and Adobe Illustrator software.
Extra techniques and materials will be assigned based on each person’s project needs; the use of classic drawing material or digital drawing material may be necessary and must be kept available for the duration of the course.
Learning activities
-
Covering essential technical knowledge of textile printing, including inkjet/sublimation printing, screen printing, transfer techniques, CMT placement, compositional schemes, color management, and quality control.
-
Hands-on projects to practice image manipulation, software usage, and the integration of mixed media to produce compelling graphic results. The focus will be on mastering the tools most useful in print design.
-
Each student will work on their own thesis project, developing graphic motifs and prints based on prior research and new material. Students will explore how to create a unique graphic and color identity, ensuring professional-quality prints.
Definition of Print Design
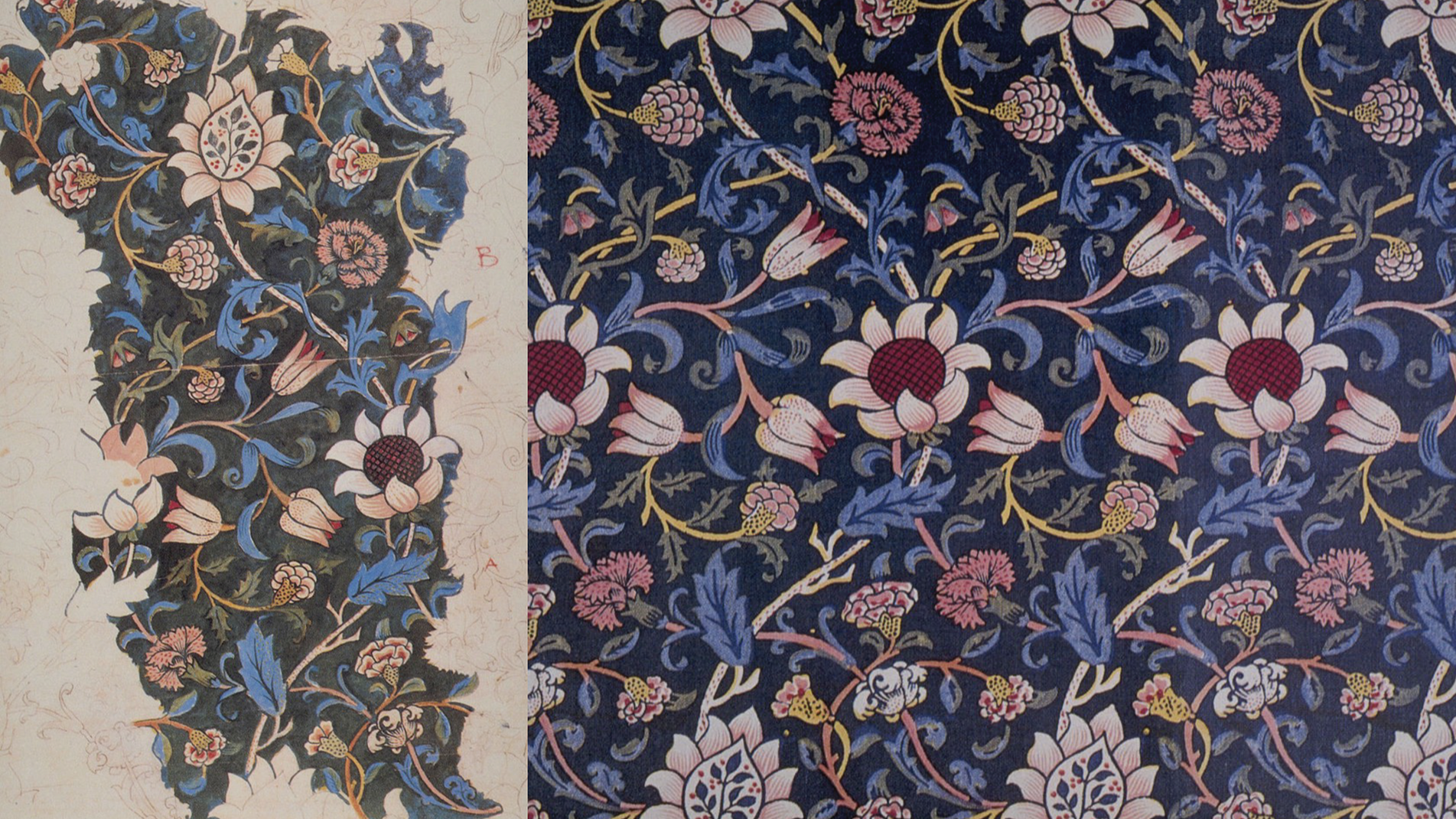
Print design in fashion involves the creation of decorative patterns, motifs, or images that are applied to fabrics or garments. These prints can range from simple geometric shapes to intricate illustrations.
Prints play a crucial role in fashion by adding uniqueness, storytelling, and aesthetic appeal to clothing.
A variety of different types of prints exist in fashion industry. Each type serves a distinct purpose and requires specific design considerations.
About Print Design
What is Textile Printing?
Process of applying color to fabric in specific patterns or designs.
Unlike dyeing, which colors the entire fabric uniformly, printing applies color to selected areas.
Properly printed fabrics resist washing and friction due to strong bonding between dye and fiber.
ALLOVER PRINT / SEAMLESS PATTERN
SOFT ACCESSORIES
PLACED PRINT / ENGINEERED PRINT
MIXED TECHNIQUE
Printing Techniques
Various printing techniques are employed in the fashion industry to transfer designs onto fabrics.
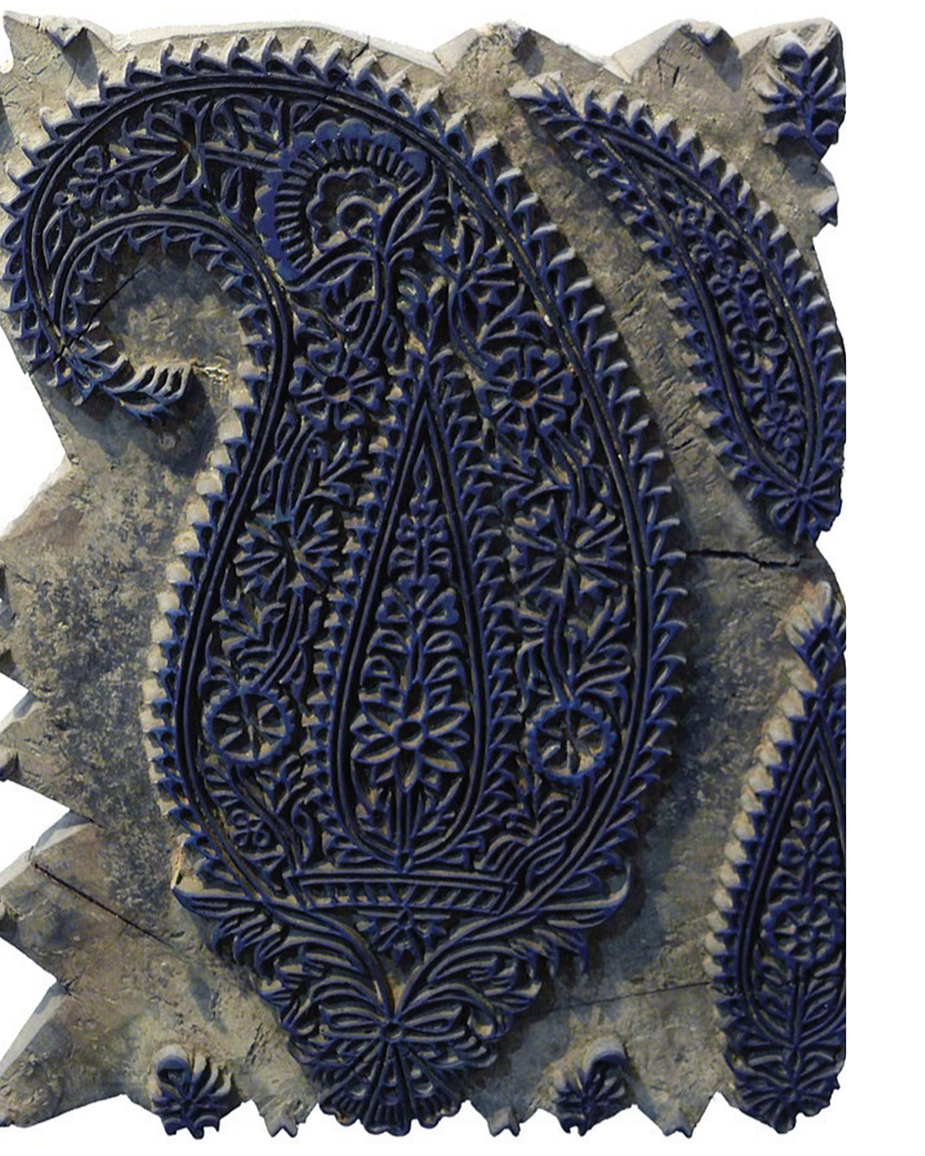
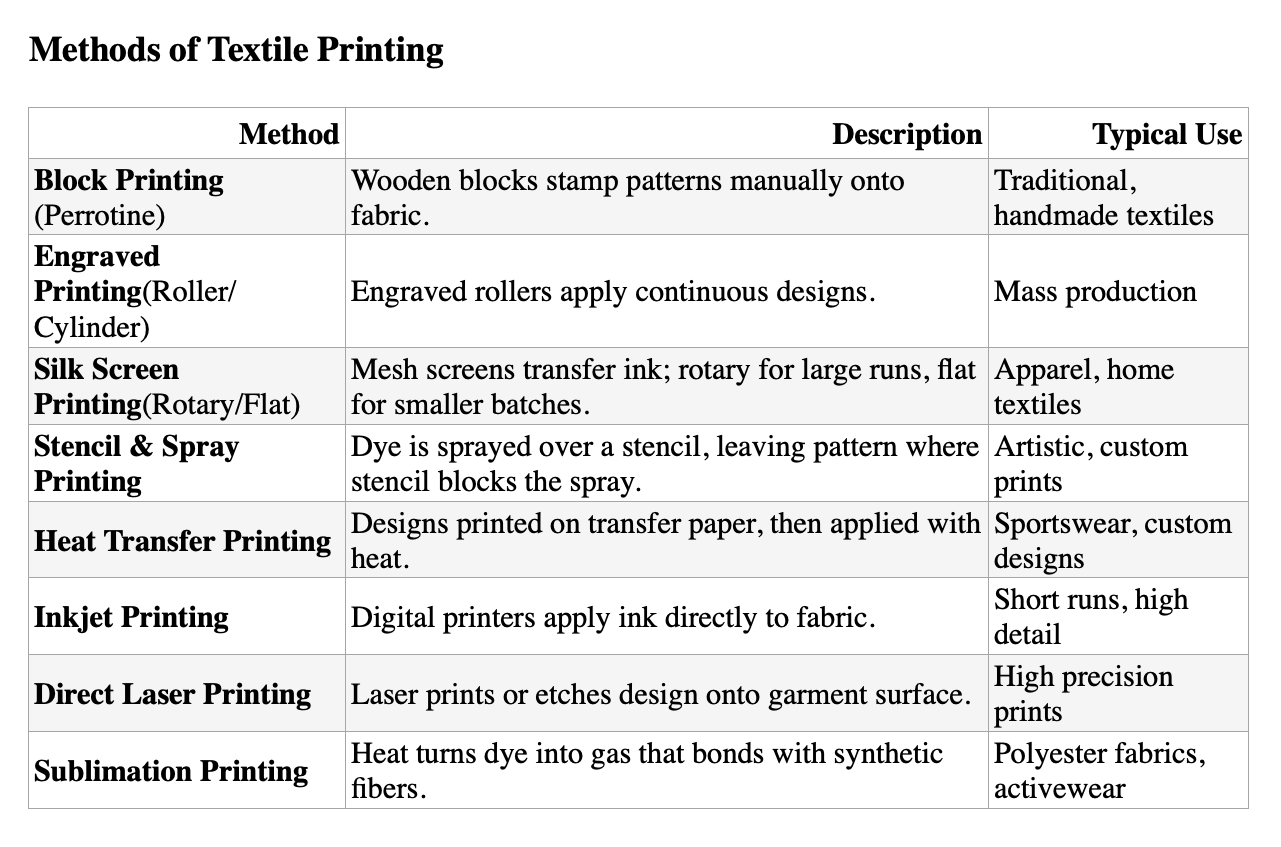
1. Block Printing
Block printing is one of the oldest and simplest textile printing methods. It uses blocks made of wood, copper, or other materials, carved with a design. Dye is applied to the raised surface of the block, which is then pressed onto the fabric to transfer the pattern.
Each color in the design requires a separate block. The block maker carves the design, starting with larger areas and finishing with fine details to prevent damage. Intricate lines that are difficult to carve in wood are created using thin strips of brass or copper, bent and embedded into the block — a technique known as coppering.
Block printing is a slow, labor-intensive process, typically done by hand. The perrotine, a block-printing machine invented by Perrot of Rouen in 1834, mechanized the process but is now of historical interest only.
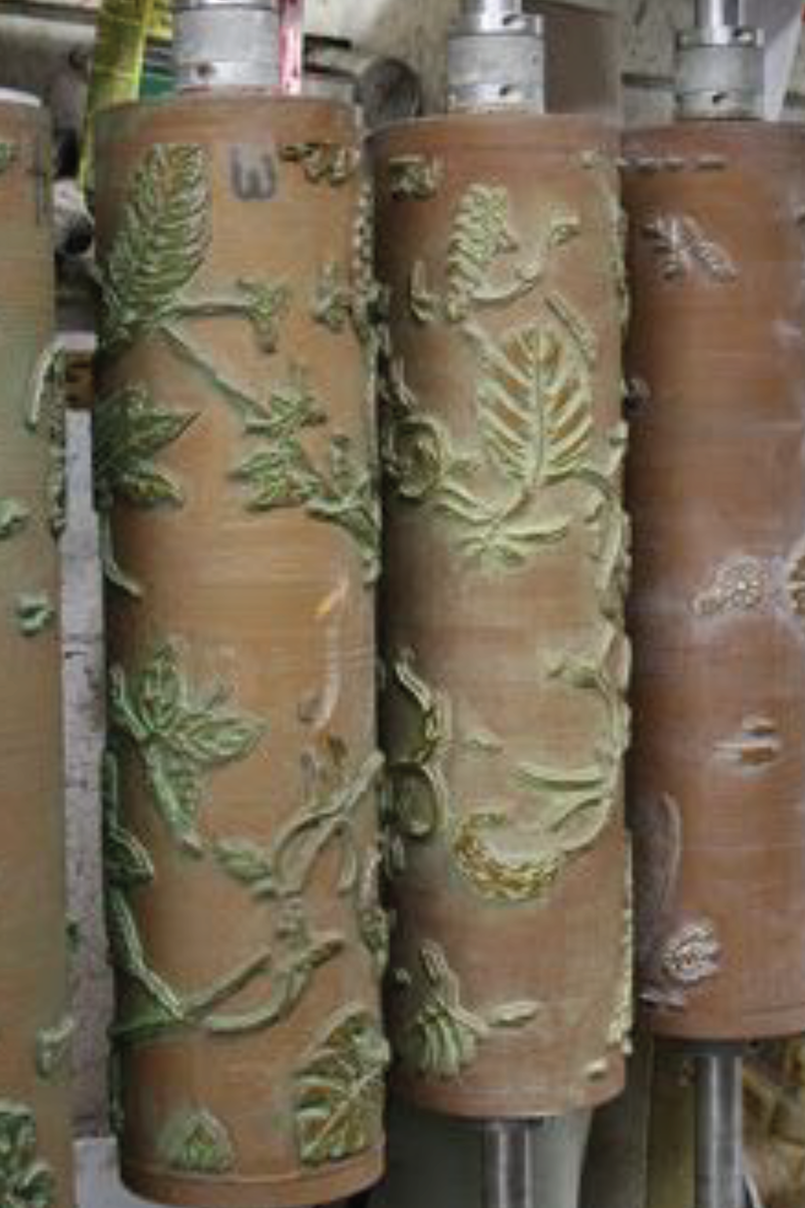
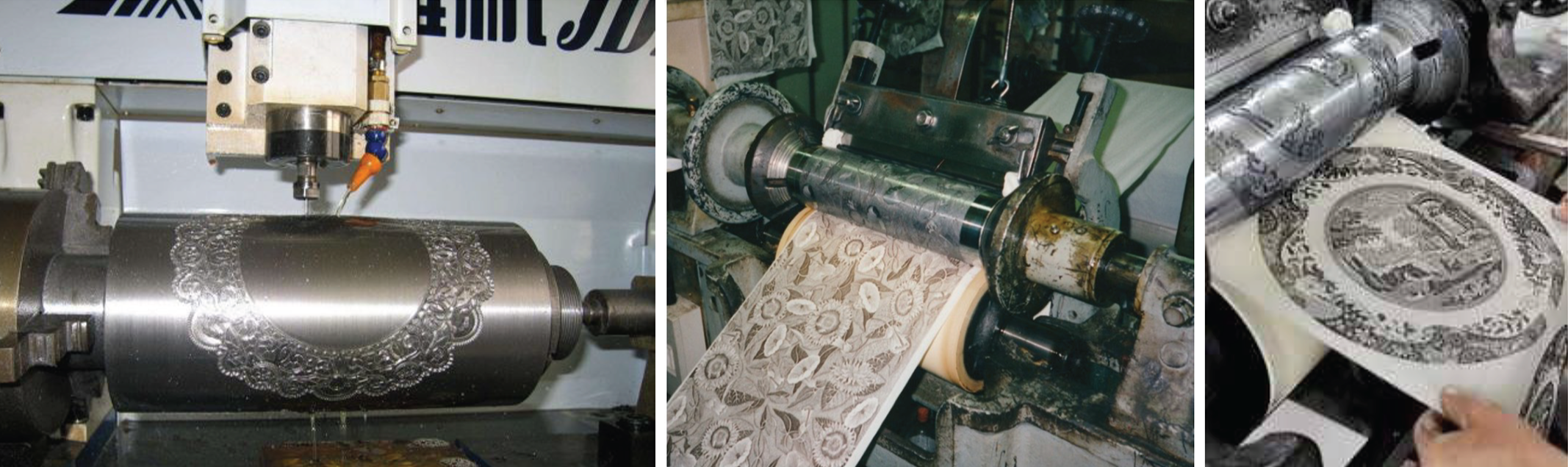
2. Engraved Roller Printing
Engraved roller printing uses engraved metal rollers to apply dye as fabric passes through the printing machine. This method produces most of the printed fabrics used in clothing and textiles today.
Each color requires a separate roller, allowing for consistent, high-quality prints across large quantities. After printing, the fabric is dried and steamed to fix the dye.
The process was patented by Thomas Bell in 1785, who first used engraved plates for textile printing. Bell's machine could print six colors simultaneously, but early versions struggled to align the rollers correctly. Adam Parkinson of Manchester solved this issue the same year, making multi-color roller printing commercially viable.
3. Silk Screen Printing
Silk screen printing, also known as screen printing or serigraphy, uses a mesh screen to transfer ink onto fabric. Traditionally, silk was used for the mesh, but today synthetic threads are more common.
A stencil blocks out areas where ink is not desired. A squeegee moves across the screen, pressing ink through the open mesh onto the fabric. As the screen lifts, the ink transfers to the fabric. Since only one color is printed at a time, multiple screens are used for multi-colored designs.
Design files for screen printing are created in solid colors, with separate layers for each color.
Types of Screen Printing:
• Flat Screen Printing — manual or semi-automatic, suitable for small runs and detailed work.
• Rotary Screen Printing — uses cylindrical screens for continuous, high-speed production.
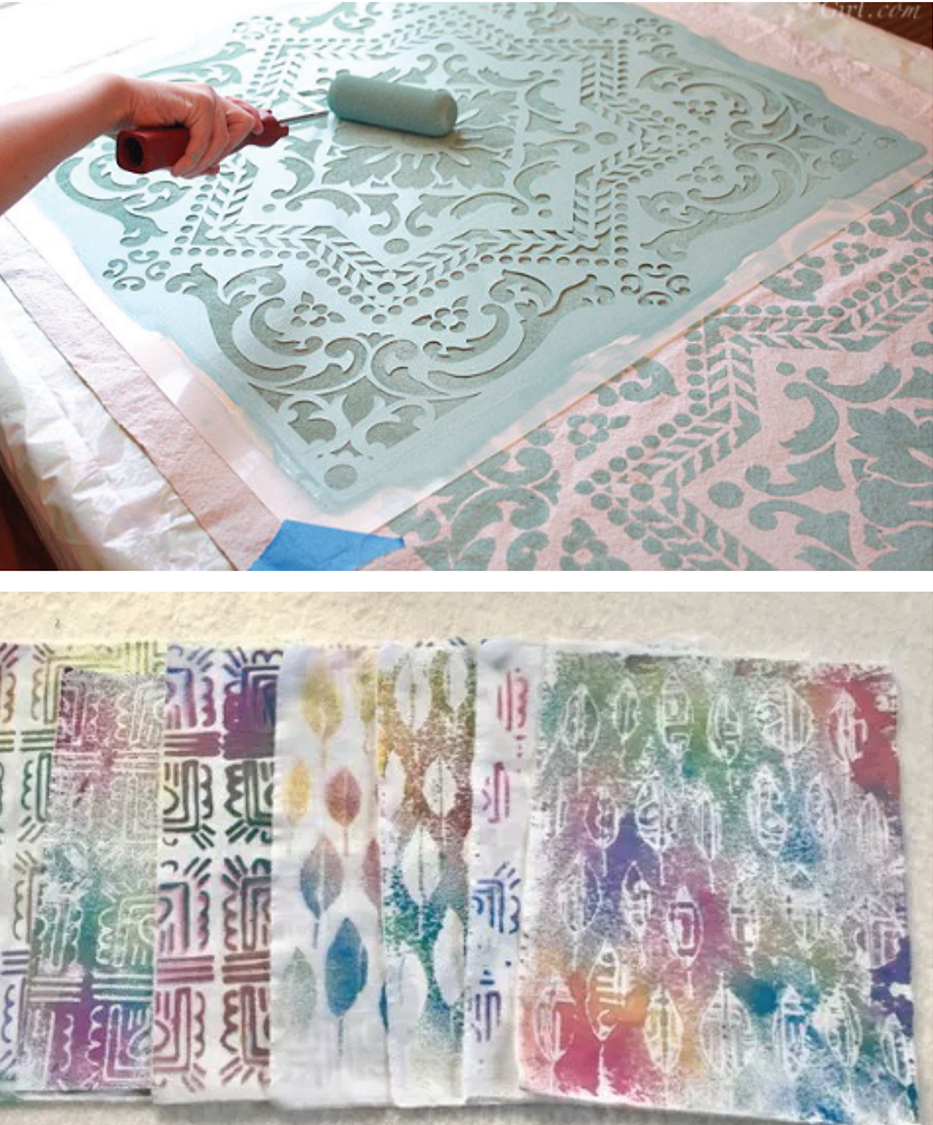
4. Stencil and Spray Printing
Stencil and spray printing uses stencils cut from materials like metal, wood, paper, or plastic to create designs. Dye or color is applied through the cut-out areas onto the fabric.
This method is simple and easy—even children can do it—but it is labor-intensive and slow, making it mostly suitable for small-scale or single-use projects.
In spray printing, specialized spray guns force dye through screens or stencils to transfer color onto fabric. Spray techniques are often combined with stencil use for greater control.
5. Heat Transfer Printing
Heat transfer printing uses a printing machine and heat press to transfer designs onto fabric. It’s a cost-effective method widely used for printing logos and messages on thousands of garments like t-shirts.
The design is first printed on special transfer paper, then transferred to the fabric by passing both through heated rollers.
However, this method has drawbacks: the dye often doesn’t fully penetrate the fabric, causing the fabric to show through the design. Colors may fade after washing, and transfers can peel or crack. The fabric surface may feel rough, and sometimes the edges of the transfer paper are visible.
6. Inkjet Printing
Digital textile printing began in the late 1980s as an alternative to traditional screen printing. The development of dye-sublimation printers in the early 1990s allowed direct printing on fabric using sublimation and disperse inks, eliminating the need for transfer paper.
The future of textile printing is digital, offering greater speed, quality, and efficiency. Recent innovations in water-based inkjet inks enable printing on a wide range of fabrics—such as cotton, blends, nylon, rayon, and silk—with simpler fixation processes.
These pigmented inks match the color and wash fastness of screen prints while improving fabric feel. Inkjet printing supports complex designs with multi-color layering and shading, making it ideal for designing, sampling, and short runs.
7. Inkjet Direct Print on Garment
Direct-to-garment (DTG) printing is a digital inkjet method that applies colorants directly onto fabric. It is used both for small designs on individual garments and larger prints on textile rolls.
The main advantage of DTG printing is the ability to produce realistic, high-quality images at low cost—even for small print runs or one-off items.
8. Sublimation Printing
Sublimation printing uses heat to transfer sublimation dyes onto fabric, requiring an inkjet or laser printer, sublimation ink, and a heat press.
Though more expensive than heat transfer due to costly inks, sublimation produces vivid, attractive prints. However, it only works well on synthetic fabrics like 100% polyester; cotton requires a special coating to accept the print.
While sublimation prints are generally very durable, they can fade with prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
Market Trends and Branding
Role of Print Design: